자바의정석 Chapter8. 예외처리
프로그램 에러
- 프로그램이 실행 중 어떤 원인에 의해서 오작동을 하거나 비정상적으로 종료되는 경우를 프로그램 에러라고 합니다.
에러의 종류
- 컴파일 에러 - 컴파일 시에 발생하는 에러
- 런타임 에러 - 실행 시에 발생하는 에러
- 논리적 에러 - 실행은 되지만, 개발자의 의도와 다르게 동작하는 에러
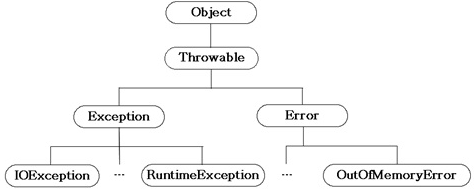
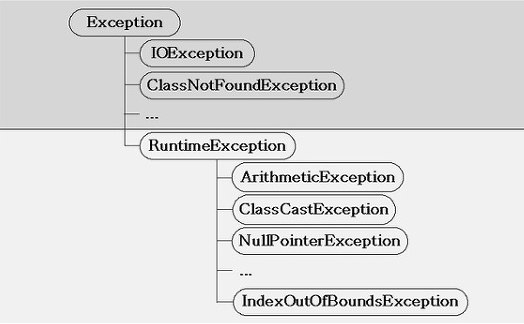
예외 클래스의 계층구조
모든 예외의 최고 조상은 Exception클래스 입니다.
try catch finally
- 프로그램 실행 시 발생할 수 있는 예기치 못한 예외의 발생을 대비한 코드를 작성하는것을 예외처리라고 합니다.
- 프로그램의 비정상 종료를 막고 실행상태를 유지 합니다.
- try - 예외가 발생할 가능성이 있는 문장
- catch - 예외처리를 위한 문장
- finally - 예외의 발생여부에 관계없이 반드시 수행되어야 하는 문장
class ExceptionEx {
public static void main(String[] args){
try {
// 예외가 발생할 가능성이 있는 문장
} catch {Exception e) {
// try{} 에서 예외 발생 시 예외처리를 위한 문장
} finally {
// 예외의 발생여부에 관계없이 반드시 수행되어야 하는 문장
}
}
}
printStackTrace()
예외발생 당시의 호출스택에 있었던 메서드의 정보와 예외 메시지를 화면에 출력합니다.
getMessage()
발생한 예외클래스의 인스턴스에 저장된 메시지를 얻을 수 있습니다.
멀티 catch블럭
JDK1.7부터 여러 catch블럭을 ‘|’ 기호를 이용하여 하나의 catch블럭으로 합칠 수 있게 되었습니다.
[AS-IS]
try {
...
} catch (ExceptionA e} {
...
} catch (ExceptionB e} {
...
}
[TO-BE]
try {
...
} catch (ExceptionA | ExceptionB e) {
...
}
예외 발생시키기
throw 지시어를 이용하여 강제로 예외를 발생시킬 수 있습니다.
[예제]
try {
System.out.println("try : 예외 발생 전");
throw new Exception("강제 예외 발생");
System.out.println("try : 예외 발생 후");
} catch (Exception e} {
System.out.println("exception : " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
System.out.println("finally : 종료");
}
[실행 결과]
try : 예외 발생 전
exception : 강제 예외 발생
finally : 종료
메서드에 예외 선언하기
메서드내에서 try catch finally 와 같이 직접 예외를 처리 하는 방법 이외에 메서드에 throws 를 선언하여 자신을 호출한 메서드에게 예외를 던질 수 있습니다.
[예제]
void method1() {
try {
System.out.println("method1 : 예외 발생 전");
method2(); // 오류 발생
System.out.println("method1 : 예외 발생 후");
} catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
} finally {
System.out.println("method1 finally : 종료");
}
}
void method2() throw Exception {
System.out.println("method2 : 예외 발생 전");
throw new Exception("method2 : 강제 예외 발생");
System.out.println("method2 : 예외 발생 후");
}
[예제]
method1 : 예외 발생 전
method2 : 예외 발생 전
method2 : 강제 예외 발생
method1 finally : 종료
사용자 정의 예외 만들기
Exception 객체를 상속하여 새로운 예외 클래스를 정의 할 수 있습니다.
public class AksException extends Exception {
private final String errCd;
private final String errMsg;
public AksException(String errCd) {
super(getMessage(errCd));
this.errCd = errCd;
this.errMsg = getMessage(errCd);
}
public AksException(String errCd, String[] arg) {
super(getMessage(errCd, arg));
this.errCd = errCd;
this.errMsg = getMessage(errCd);
}
public AksException(String errCd, Throwable th) {
// WAS - DB 세션 타임아웃시 다르게 표시되도록 예외처리
//super(getMessage(th.toString().indexOf("SQLTimeoutException") > -1 ? "gsi.cm.err.sqlTimeout" : errCd), th);
super(getMessage(errCd), th);
this.errCd = errCd;
this.errMsg = getMessage(errCd);
}
/**
* 에러메세지 리턴
* @Method Name : getErrorMessage
* @return
*/
public String getErrCd() {
return errCd;
}
public String getErrMsg() {
return errMsg;
}
public static String getMessage(String errCd) {
if(errCd != null && errCd.indexOf(";;")> 0) {
String[] arrMsg = errCd.split(";;");
String[] param = {};
if(arrMsg.length > 1 && arrMsg[1] != null ) {
param = arrMsg[1].split("##");
}
return "MessageUtil Not found";
} else {
return "MessageUtil Not found";
}
}
public static String getMessage(String errCd, String[] arg) {
return "MessageUtil Not found";
}
}
Reference
자바의 정석

댓글남기기